Tutorial 3 - Create table using wizard
Step 0 - Start Wizard
This tutorial show, how to create new table using wizard in KPoGre. Wizard is not able to
handle all possible requirements, but it is suitable for most of common situations. I expect, that
you are basicaly familiar with CREATE TABLE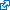 statement.
statement.
In left tree view, select ![]() Database
Database![]() Schema
SchemaDatabase -> ![]() Wizard
Wizard![]() table
table

Or select Tables folder and make right button click on it to display
object menu.

KPoGre displays wizard for create new table. This wizard have 7 steps.
Step 1 - Table name
If you start this wizard when Database is selected,
choose schema for new table. When you run wizard from Schema or
Tables folder, actual schema is used.
Type name for new table. The Tablespace is the name of the tablespace in which the new table is to be created. If not supplied, the default tablespace of the table's schema will be used. If you need new table Without OIDs, choose this option.

Step 2 - Define columns
In this step, user define list of table columns. Each column have name, datatype and another optional properties.
First, type column name. This name must be unique in table. Next choose datatype
from combo box. Short description is displayied in line under combobox. Column can be build in type or domain or user defined type. If you want to use domain or type from different namespace, use Schema combobox to list them.
If you can create multidimensional column, choose number of Array dimensions greather than 0.
Some variable lenght datatypes requires Size. And some datatypes requires
Precision and Scale.
-
Not NULL- The column is not allowed to contain null values.Unique- Specifies that a column may contain only unique values.Default- Default value for INSERT operation, when value is not specified. UseQuotedcheckbox for setting if default value is text, or leave it unchecked if default value is function, e.g. now(). For simply set current datetime value as default, useNowbutton.Check- The CHECK clause specifies an expression producing a Boolean result which new or updated rows must satisfy for an INSERT or UPDATE operation to succeed.

When you have all information for new column, press Add button. Column
may be removed from list and user may change order of columns. After defining all columns press
Next button.
Step 3 - Define table constraints
Create constraints is optional. Table may have one (and only one) primary key, and zero or more of foreign keys. Create primary key is good practice. Select type of new constraint in combo box.
Primary key
Select column in Available columns list and press Add.
If you need multicolumn primary key, repeat this step for another columns. After
adding first column, primary key name is automatically filled from table name.
You may change this name.
Optionally select Tablespace in which the index associated with a PRIMARY KEY constraint will be created. If not supplied, the index will be created in the same tablespace as the table.

Then, press Add button in Table constraints group box.

Foreign key
First select referenced table and their unique. This may be primary key
or unique index. Then select column in Available columns list and press
Add button.
Columns in FK columns and in Referenced columns must be
compatible regards datatypes, and columns number must match.
User may specify another optional properties for foreign key. See at PostgreSQL documentation, if you don't understand those parameters.

Then, press Add button in Table constraints group box.

Constraint may be removed from list, using Delete button. After defining all constraints press
Next button.
Unique
Select column in Available columns list and press Add.
If you need multicolumn unique, repeat this step for another columns. After
adding first column, unique name is automatically filled from table name.
You may change this name.
Optionally select Tablespace in which the index associated with a UNIQUE constraint will be created. If not supplied, the index will be created in the same tablespace as the table.

Then, press Add button in Table constraints group box.

Unique may be removed from list, using Delete button. After defining all constraints press
Next button.
Check
Type an Expression producing a Boolean result which new or updated rows must satisfy for an insert or update operation to succeed. Expressions evaluating to TRUE or UNKNOWN succeed. Should any row of an insert or update operation produce a FALSE result an error exception is raised and the insert or update does not alter the database. A check constraint specified as a column constraint should reference that column's value only, while an expression appearing in a table constraint may reference multiple columns.
If you doubleclick on column in Available columns list, it is inserted to Expression edit line to current cursor position

Then, press Add button in Table constraints group box.

Check may be removed from list, using Delete button. After defining all constraints press
Next button.
Step 4 - Define table indexes
Create indexes is optional. Indexes are primarily used to enhance database performance.
Select column in Available columns list and press Add button.
If you need multicolumn index, repeat this step for another columns. After
adding first column, Index name is automatically filled from table and first column name.
You may change this name.
If you create Unique index, check this option.
Optionally select Tablespace where the index will be created. If not supplied, the index will be created in the same tablespace as the table.

Then, press Add button in Table indexes group box.

Expression Index
An index field can be an expression computed from the values of one or more columns of the table row. This feature can be used to obtain fast access to data based on some transformation of the basic data.

For example, an index computed on upper(first_name) would allow the clause WHERE upper(first_name) = 'JIM' to use an index. Select this function in combobox.
Note: Functions list is refreshed, each time is Index columns list changed. Listed are
only "immutable" functions with number of parameters as index columns count.

Partial Index
When the WHERE predicate is present, a partial index is created.

Type WHERE clause that define partial data for index.

Index may be removed from list, using Delete button. After defining all indexes press
Next button.
Step 5 - Define user rights
This step allow grant specific privileges on table to one or more users or groups of users. These privileges are added to those already granted, if any.
Select users or groups (multiple select allowed) or check PUBLIC for grant to all users.
Check one or more privileges, or ALL.
Click on Add button. One or more grant commands is inserted to list.
Grant privilege may be removed from list, using Delete button.
After defining all privileges press Next button.

Step 6 - Review SQL statement
In this step, SQL statement for create table, indexes and grant privileges is displayied for your check. You may modify it, if you understand, what do you do.

When you press Next button command will be send to server.
Step 7 - Check operation result
Finally, check operation result. If you get any error, you may go Back
and try make changes and retry step 6.

Press Finish button and start discovery newly created table.
